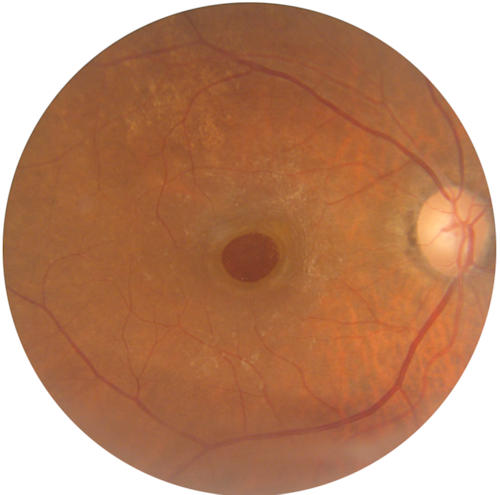
What is Macular Hole?
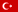
It is a hole that occurs in the macula, a 3-4 mm area in the center of the retina responsible for central vision and light sensitivity.What are the Risk Factors for Macular Hole Development?
Macular hole typically occurs with advanced age, as the vitreous, the fluid inside the eye, separates from the macula. Additionally, it can develop due to high myopia, eye traumas, retinal tears or detachments, intraocular infections, and traction caused by an epiretinal membrane on the macula. Its incidence increases with age.What are the Symptoms of Macular Hole?
In the presence of a macular hole, there may be differences in the shape and size of objects, and distorted or bent vision problems. There may be a decrease in visual acuity to varying degrees, which can remain unchanged for many years.How is Macular Hole Diagnosed?
It can be detected through dilated fundus examination after applying pupil-dilating drops. Imaging techniques such as Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FFA) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) are important in detecting macular holes and determining possible associated findings.OCT is a laser-based imaging method that scans the central vision area in thin sections and provides quick results. The presence of a macular hole is best detected with OCT. Additionally, it is highly beneficial in evaluating the presence of macular edema, epiretinal membrane, and traction.
FFA is a non-radiating angiography performed by injecting contrast material into the patient's forearm, allowing for better examination of the retinal vascular structure.
How is Macular Hole Treated?
If the macular hole has caused a significant decrease in vision or is causing visual symptoms, surgical treatment is required.Surgery involves vitrectomy, during which the internal limiting membrane in the macular area is completely peeled off or a flap is created and removed. After surgery, gas is injected into the eye, and the patient is required to maintain a face-down position for 5-7 days. The gas usually dissipates and disappears within 1 month. Traveling to high altitudes and flying are prohibited until the gas is completely removed from the eye.
Depending on the stage of the hole, timely and appropriate intervention can lead to visual improvement.